As a power source for low-power electronic products (mostly battery powered products), USB provides more and more application opportunities, and the ubiquitous USB also provides more opportunities and greater challenges for charger design. This article introduces the simple connection between a battery charger and a USB power supply, elaborates on the characteristics of the USB power bus and the related technologies, charging methods, and termination charging methods of NiMH and Li+batteries, and provides a complete example of NiMH intelligent battery charging through a USB port.
A Universal Serial Bus (USB) port is a bidirectional data port with power and ground. USB can connect all types of peripheral devices, including external drives, storage devices, keyboards, mice, wireless interfaces, cameras and cameras, MP3 players, and countless electronic devices. Many of these devices are powered by batteries, some of which come with built-in batteries. For battery charging design, the widely used USB brings both opportunities and challenges. This article explains how to interface a simple battery charger with a USB power supply. The article covers the characteristics of USB power bus, including voltage, current limitation, surge current, connectors, and cable connection issues. It also introduces nickel hydrogen battery (NiMH) and lithium battery technology, charging methods, and charging termination technology. A complete example circuit is provided to achieve intelligent charging of NiMH batteries through USB ports, and charging data is provided.
USB features
The USB bus can provide power for low-power electronic devices. The bus power supply is isolated from the power grid and has good stability. However, the available current is limited, and there are potential interoperability issues between the load and the host or power supply.
Battery charging requirements
1、Single cell lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries
Nowadays, when lithium batteries are charged to their maximum rated capacity, their voltage is usually between 4.1V and 4.2V. The voltage range of newer and larger capacity batteries currently on the market is between 4.3V and 4.4V. Typical prismatic lithium-ion (Li+) and lithium polymer (Li Poly) batteries have capacities ranging from 600mAh to 1400mAh.
For Li+and Li Poly batteries, the preferred charging curve is to start from constant current charging and continue until the battery voltage reaches the rated voltage. Then, the charger adjusts the voltage at both ends of the battery. These two adjustment methods constitute the constant current (CC) and constant voltage (CV) charging method. Therefore, this type of charger is commonly referred to as a CCCV charger. After the CCCV charger enters CV mode, the charging current of the battery begins to decrease. If a typical charging rate of 0.5C to 1.5C is used for charging, the charger will switch from CC mode to CV mode when the battery reaches 80% to 90% of its full capacity. Once the charger enters CV charging mode, it monitors the battery current; When the current reaches the minimum threshold (a few milliamps or tens of milliamps), the charger terminates charging. The typical charging curve of lithium batteries is shown in the figure.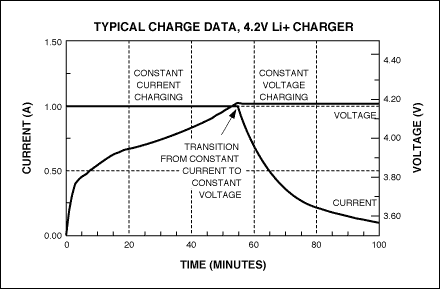
From the USB voltage drop indicator, it can be seen that the downstream low-power port voltage of the port power hub does not have sufficient margin, making it difficult to charge the battery to 4.2V. A small amount of additional resistance on the charging path can hinder normal charging. Li+and Li Poly batteries should be charged at appropriate temperatures.
The maximum charging temperature recommended by the manufacturer is usually between+45 ° C and+55 ° C, and the maximum allowable discharge temperature can be increased by about 10 ° C. The materials used in these batteries have very active chemical properties, and if the battery temperature exceeds+70 ° C, combustion will occur. Lithium battery chargers should have a thermal shutdown circuit that monitors the battery temperature. If the battery temperature exceeds the manufacturer's recommended maximum charging temperature, the charging will be terminated.
2、Nickel hydrogen batteries (NiMH)
NiMH batteries are heavier than lithium batteries and have a lower energy density. NiMH batteries have always been cheaper than lithium batteries, but recently the price difference between the two has been narrowing. NiMH batteries have standard dimensions and can directly replace alkaline batteries in most applications. The nominal voltage of each battery is 1.2V, which will reach 1.5V when fully charged.
A constant current source is usually used to charge NiMH batteries. When it reaches a fully charged state, an exothermic chemical reaction occurs, leading to an increase in battery temperature and a decrease in battery terminal voltage. It can detect the rate of temperature rise or negative voltage change of the battery and be used to terminate charging. These charging termination methods are called dT/dt and- Δ V. When the charging rate is very low, dT/dt and- Δ V is not very obvious and difficult to accurately detect. When the battery begins to enter an overcharge state, dT/dt and- Δ The V response begins to show. If you continue to charge at this time, it will damage the battery.
Termination detection is much easier when the charging rate is greater than C/3 than when the charging rate is lower. The temperature rise rate is approximately 1 ° C/minute- Δ The V response is also more pronounced than at low charging rates. After the fast charging is completed, it is recommended to charge the battery at a lower current for a period of time to fully charge the battery (to make up for the charging). After the completion of the supplementary charging stage, a trickle charging current of C/20 or C/30 is used to compensate for the self discharge effect and maintain the battery in a fully charged state. Figure 3 shows the battery voltage curve of a NiMH battery (partially charged in advance) charged with a DS2712 NiMH charger. In this figure, the data of the upper curve is obtained when the charging current is flowing into the battery, while the data of the lower curve is measured when the current is cut off. In DS2712, this voltage difference is used to distinguish between NiMH batteries and alkaline batteries. If an alkaline battery is detected, DS2712 will not charge it.
summary
For battery charging of small consumer electronic devices, a USB port is an economical and practical power source. To fully comply with USB 2.0 specifications, the load connected to the USB port must be able to communicate in both directions with the host. The load must also comply with power management requirements, including low power consumption mode and means for the host to determine when to draw large currents from the port. Although partially compatible systems can accommodate most USB hosts, unexpected results may sometimes occur. Only with a good understanding of USB specification requirements and load expectations can a good balance be achieved between compatibility with specifications and load complexity.
Post time: 2023-12-28 17:22:28